| # | Topics of the chapter |
| 01 | Improtant definitions |
| 02 | Important Differences |
| 03 | Exercise Question And Answer |
Ans: A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function in an organism. Tissues help in the growth, repair, and functioning of plants and animals.
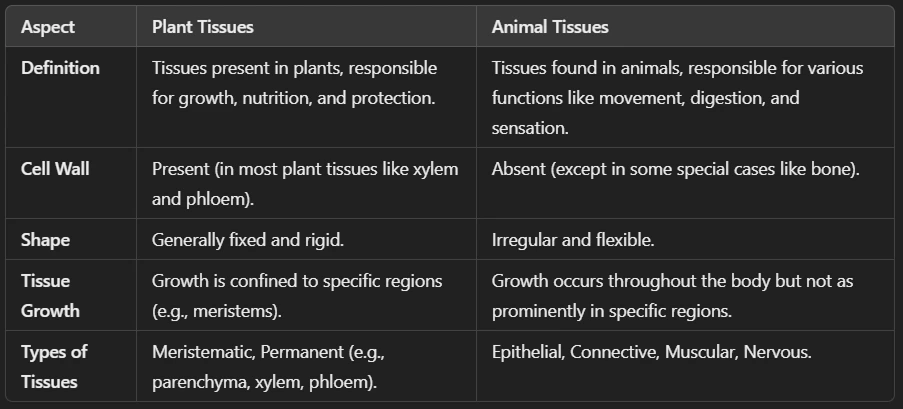
Ans: There are two types of tissues: Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues.
1️⃣ Plant Tissues:
🔹 Meristematic Tissue – Helps in plant growth
🔹 Permanent Tissue – Provides support, transport, and storage. It has also two types of tissues (Simple Permanent Tissues And Complex Permanent Tissues.)
2️⃣ Animal Tissues:
🔹 Epithelial Tissue – Covers body surfaces.
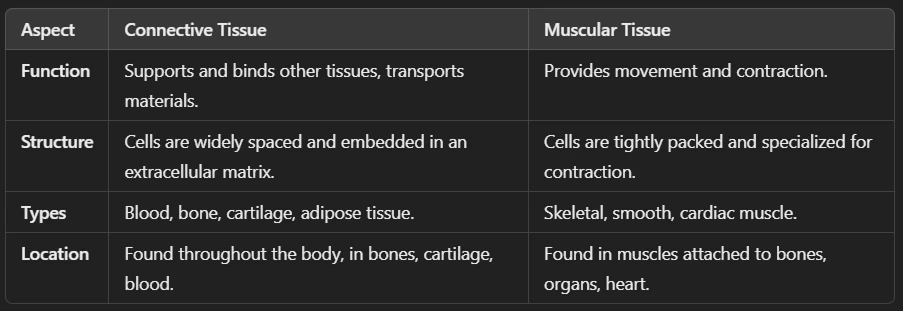
🔹 Connective Tissue – Supports and binds body parts.
🔹 Muscular Tissue – Helps in movement.
🔹 Nervous Tissue – Transmits signals.
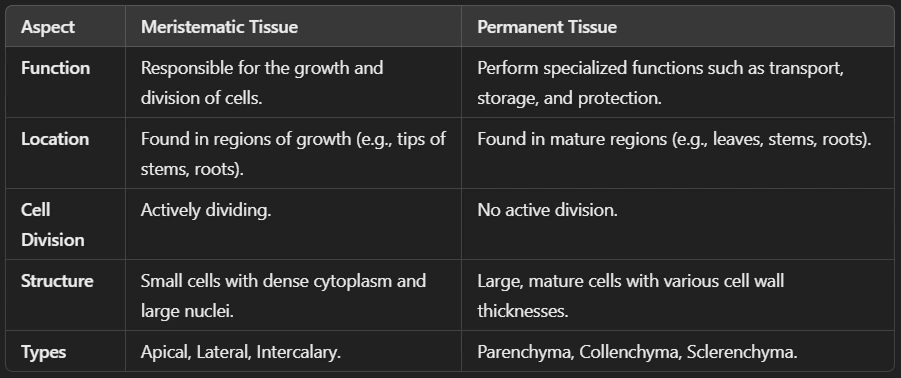
Ans: These are actively dividing cells found in growing parts of the plant, such as roots and shoot tips. Types of Meristematic Tissues are:
i. Apical Meristem: The location of this tissue is at the tips of roots and shoots, and its main function is to help in plant growth (lengthwise).
ii. Lateral Meristem: The location of this tissue is the sides of stems and roots, and its main function is to help in plant Increases thickness (secondary growth).
iii. Intercalary Meristem: The location of this tissue is at the base of leaves or nodes, and its main function is to helps in regrowth of grass and other monocots.
Ans: These are non-dividing mature tissues that help in support, transport, and protection.
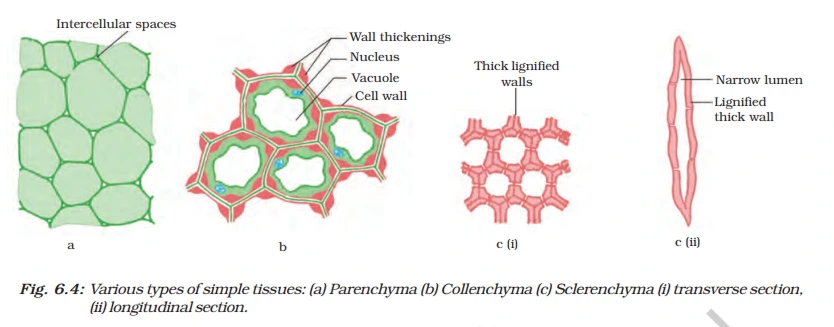
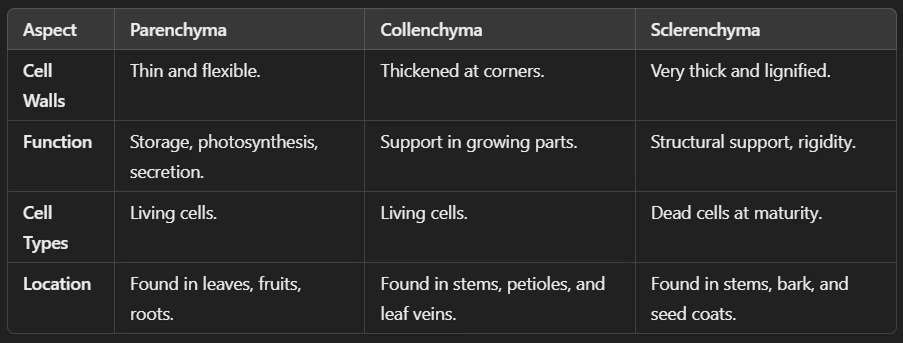
i. Simple Permanent Tissue: This is made up of only one type of cell. There are three types of Permanent Tissues as:
(a.) Parenchyma – Stores food, provides support, and helps in photosynthesis. Example: Potato (Stores starch)
(b.) Collenchyma – Provides flexibility (present in leaf stalks). Example: Celery stalks
(c.) Sclerenchyma – Provides rigidity and strength (found in hard seeds and bark). Example: coconut husk (fibers).
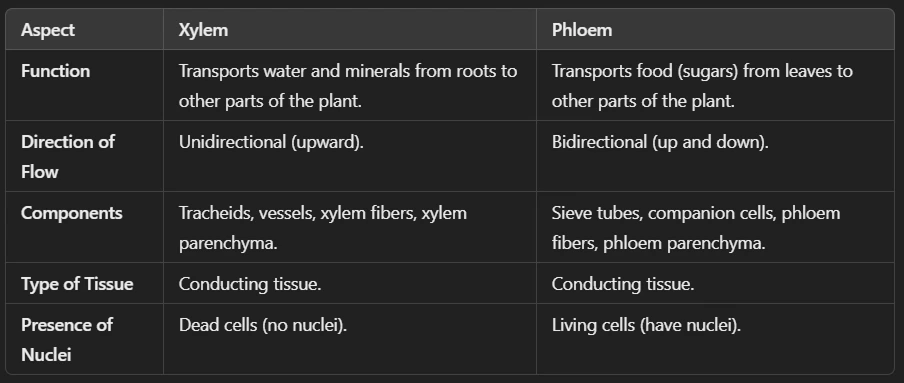
ii. Complex Permanent Tissue: This type of tissues are made of different types of cells working together for transport. There are 2 types of complex tissues
(a.) Xylem – Transports water and minerals from roots to leaves. Xylem vessels help trees take water from roots to leaves.
(b.) Phloem – Transports food (sugar) from leaves to other parts. Phloem transports glucose from leaves to stems and roots.
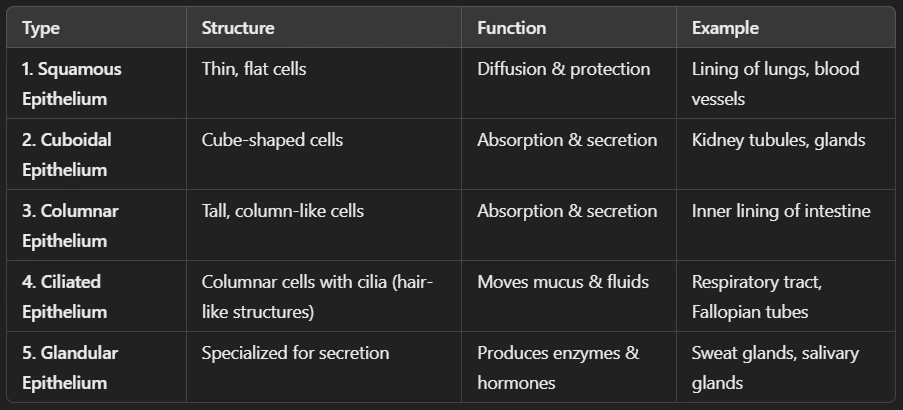
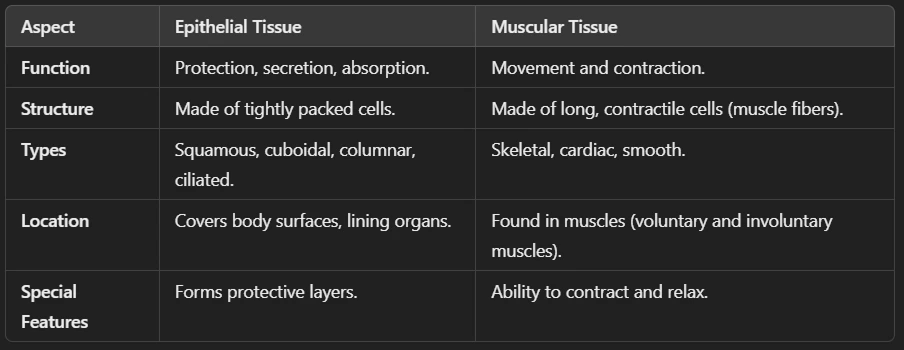
Ans: Epithelial tissue is a type of animal tissue that covers the body surfaces, lines internal organs, and forms glands. It acts as a protective barrier and helps in absorption, secretion, and filtration. There are the following Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue:
✅ Closely packed cells with little or no space between them.
✅ No blood vessels (receives nutrients from underlying tissues).
✅ Rest on a basement membrane for support.
✅ Can regenerate quickly when damaged.
Types of Epithelial Tissues:
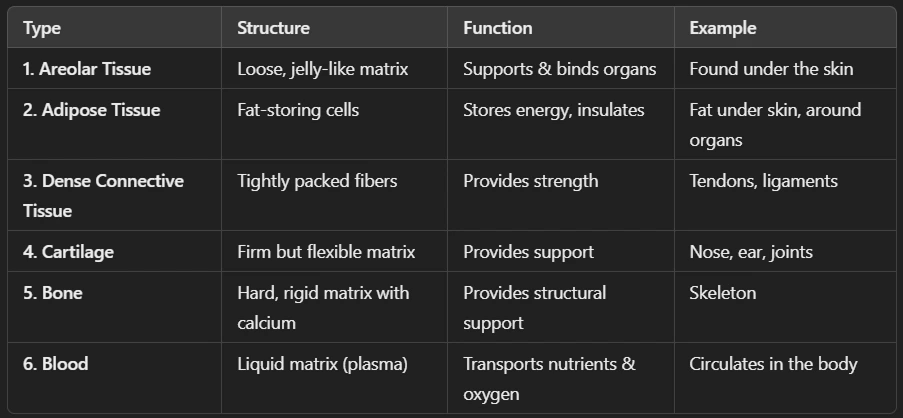
Ans: Connective tissue is a type of animal tissue that provides support, strength, and protection to the body. It connects, binds, and supports other tissues and organs.
🔹 Characteristics of Connective Tissue
✅ Widely spaced cells with a lot of intercellular material (matrix).
✅ Contains fibers (collagen, elastin) for flexibility and strength.
✅ Rich in blood supply (except cartilage, which lacks blood vessels).
✅ Supports, connects, and protects other tissues and organs.
Types of Connective Tissue
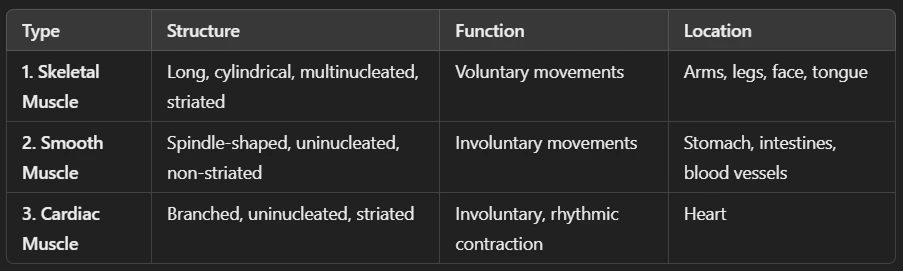
Ans: Muscular tissue is a type of animal tissue responsible for movement in the body. It is made up of muscle fibers (elongated cells) that can contract and relax, allowing movement.
🔹 Characteristics of Muscular Tissue
✅ Made of muscle fibers (long, cylindrical cells).
✅ Contains contractile proteins (actin & myosin) that help in movement.
✅ Highly vascular (rich in blood supply).
✅ Can be voluntary (controlled) or involuntary (automatic).
Ans: Nervous tissue is a specialized animal tissue responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body. It helps in receiving, processing, and responding to stimuli.
🔹 Characteristics of Nervous Tissue
✅ Made of neurons (nerve cells) and supporting glial cells.
✅ Capable of transmitting electrical and chemical signals.
✅ Highly sensitive to stimuli like touch, heat, and pain.
✅ Controls voluntary and involuntary actions.
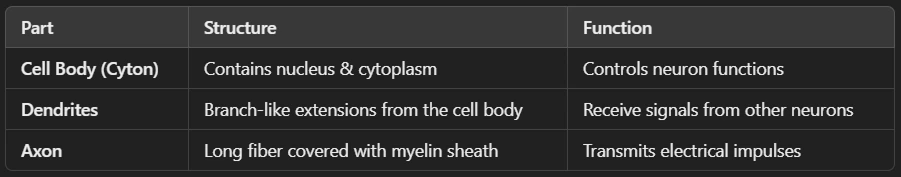
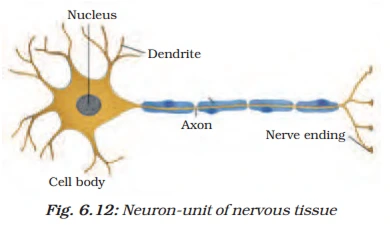
🔹 Structure of Nervous Tissue
The main functional unit of nervous tissue is the neuron (nerve cell). It has three main parts:
Ans:
Ans:
Ans:
Ans:

Ans:
Ans:
Ans:
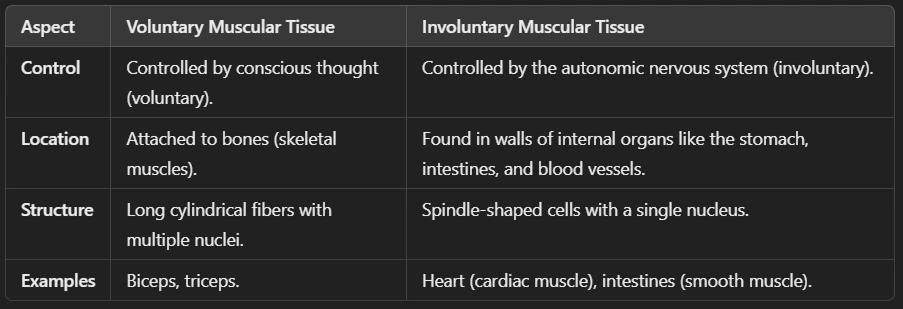
Ans:
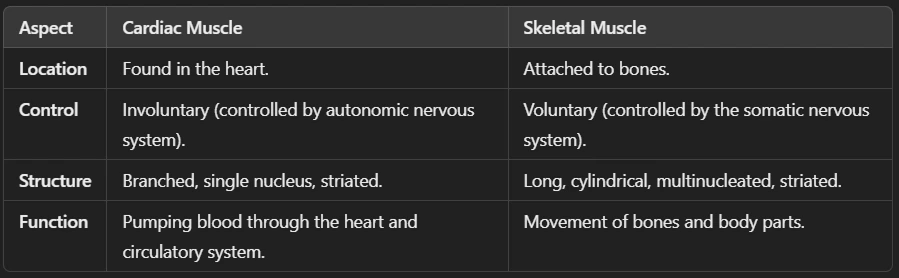
Ans:
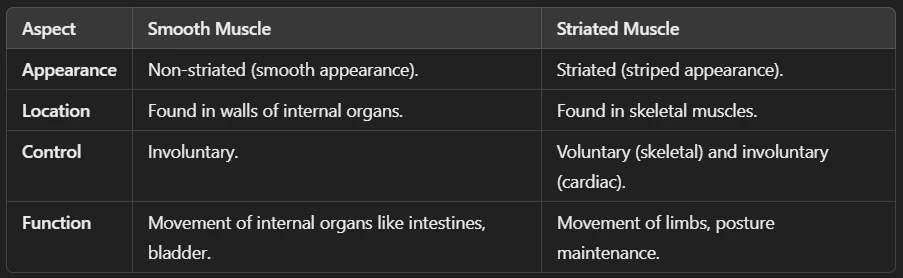
Ans: